Are you a marketer, startup founder, or motivated business owner looking for ways to get things off the ground?
Whether you need to raise brand awareness for your early-stage company or plan to launch a new product, this guide will help you understand how go-to-market strategies work and drive successful product launches.
Here’s the reality: most new ventures struggle to survive.
With 90% of startups failing and under half of all businesses making it to their fifth year, having a great product isn’t enough—you need a well-defined go-to-market plan.
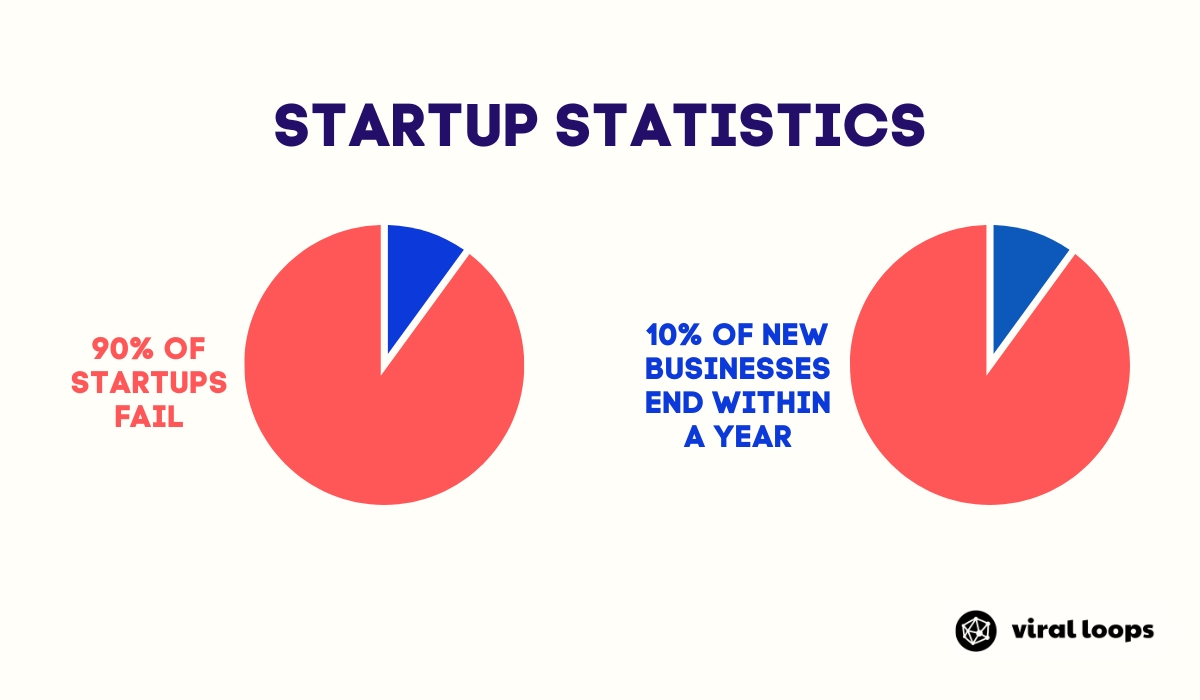
These statistics highlight why a solid GTM strategy is essential for hitting the ground running in today’s competitive landscape.
This comprehensive guide covers everything from go-to-market fundamentals to proven market strategy examples and a downloadable template that will help you establish product-market fit and achieve your business objectives.
This is going to be an in-depth GTM guide, so feel free to jump to specific sections:
- What is a Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy?
- What’s the Difference Between a Go-To-Market Strategy and a Marketing Strategy?
- Types of Go-to-Market Strategies
- 5 Go-to-Market Strategy Examples to Inspire You
- How to Build a Go-to-Market Strategy for Your Startup
What is a Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy?
A go-to-market strategy is your tactical roadmap for successfully launching a new product or entering a new market.
Think of it as your action plan that brings together all the essential pieces—from identifying your target audience to defining how you’ll reach them and convert them into customers.
The core elements of an effective GTM strategy include several critical components that work together to create a comprehensive launch plan:
- Target audience identification – Who exactly will buy your product or service and what are their specific characteristics?
- Value proposition development – Why should they choose you over competitors and what unique benefits do you offer?
- Customer acquisition strategy – How will you reach and convert prospects into paying customers?
- Buyer persona creation – What are your ideal customers’ demographics, behaviors, and decision-making processes?
- Messaging framework – What key messages will resonate with your audience across different touchpoints?
- Distribution channels – Where and how will customers access your product, and what channels work best for your target market?
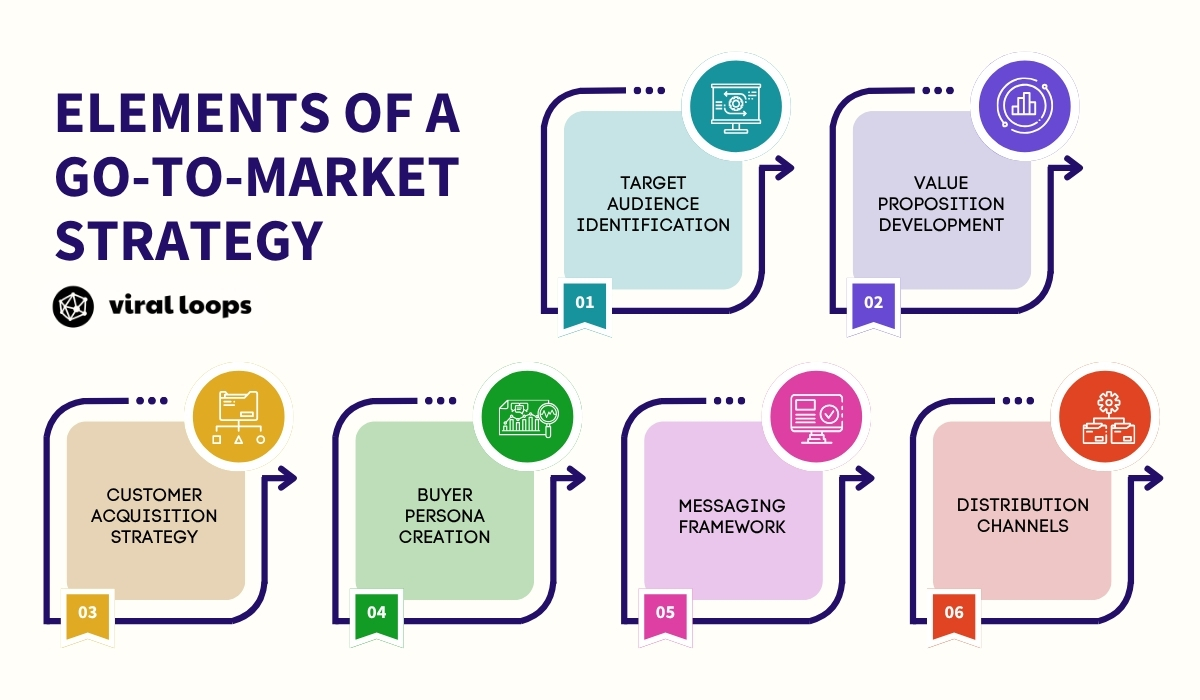
A successful go-to-market plan addresses fundamental questions about:
- product-market fit (how well your product meets market demand)
- customer identification
- competitive positioning, and
- distribution
All while aligning your marketing and sales teams around a unified approach to reaching prospective customers.
Modern go-to-market strategies have evolved beyond simple product launches to encompass comprehensive frameworks that consider the entire customer experience, from first awareness through long-term retention and advocacy.
Today’s companies use go-to-market strategies to launch new products in existing markets, bring current products to new markets, or test entirely new ventures to expand their customer base and market presence.
The digital landscape has transformed how businesses approach go-to-market planning, requiring strategies that account for multiple marketing channels, complex buyer journeys, and diverse distribution options.
Social media, content marketing, email marketing, and digital advertising have become essential components of successful go-to-market execution, helping businesses reduce customer acquisition costs (the amount spent to gain each new customer) while improving their sales funnel performance and conversion rates.
Successful go-to-market strategies also consider timing, resource allocation, and market conditions while providing clear key performance indicators for measuring success and return on investment.
They include contingency plans for different scenarios and remain flexible enough to adapt based on market research feedback and performance data from your marketing and sales teams.
The best go-to-market strategies balance immediate launch objectives with long-term growth goals and customer relationship building.
What’s the Difference Between a Go-To-Market Strategy and a Marketing Strategy?
Many people think go-to-market strategies and marketing strategies are the same thing, but they serve distinctly different purposes.
Understanding this difference helps you choose the right approach for your specific situation and ensures your marketing team allocates resources effectively.
Marketing strategies are ongoing, comprehensive efforts that encompass your entire business approach to attracting and retaining customers:
- Cover all marketing activities across your entire business and multiple product lines
- Focus on building long-term customer relationships and sustainable brand awareness
- Include multiple campaigns, channels, and customer segments working together
- Continue indefinitely as part of your regular business operations and growth initiatives
- Aim to maintain market position and drive consistent, predictable growth over time
- Often include comprehensive marketing analysis such as SWOT analysis and detailed conducting market research
- Cover actions related to brand positioning and how to attract audiences that will appreciate and engage with your brand
Go-to-market strategies are targeted, time-bound plans that focus on specific launches or market entry:
- Focus specifically on launching new products or entering new markets with clear objectives
- Target clearly defined customer segments with specific products or services
- Have fixed timelines with clear milestones and success metrics for accountability
- Involve cross-functional teams including marketing, sales, product development, and customer service advisors
- Concentrate on achieving immediate market penetration and establishing initial customer base
- Include detailed analysis of the buyer’s journey and segmentation of audiences into sub-groups
- Focus on covering new product launches and activities around a specific product’s lifecycle
- Are based on short-term approaches targeting segments of the market interested in the specific product or service
- Cover actions related to communicating a product’s competitive advantage to potential customers
- Will generally have every step targeted toward specific buyer personas or target customers
The key distinction lies in focus and duration.
Marketing strategies build long-term brand equity across your entire business, while go-to-market strategies drive specific launch objectives and immediate market penetration for particular products or markets.
Types of Go-to-Market Strategies
Different companies require different go-to-market approaches depending on their product, target market, and business objectives. Here are the main types you should consider, each offering unique advantages for customer acquisition:
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) Strategy
This approach targets specific high-value accounts with personalized experiences designed to shorten the buying process and increase conversion rates.
Marketing and sales teams collaborate closely to create customized content, communications, and events for identified prospects in their target audience.
ABM works exceptionally well for companies selling expensive products with long sales cycles, allowing them to focus marketing efforts on the most promising potential customers rather than casting a wide net.
This strategy typically involves detailed account research, personalized outreach sequences, and coordinated touchpoints across multiple marketing channels.
Inbound Marketing Strategy
This strategy focuses on creating valuable content and experiences that naturally attract potential customers through various marketing channels.
Companies use content marketing, search engine optimization, social media marketing, and targeted advertising to draw prospects in and build trust over time.
The goal is establishing authority and thought leadership while nurturing customer relationships before prospects are ready to make purchasing decisions.
Inbound marketing works particularly well for businesses with complex products that require education and consideration before purchase, often supported by a comprehensive marketing plan.
Sales Enablement Strategy
This approach provides sales teams with the tools, content, and knowledge needed to sell effectively while reducing customer acquisition costs.
This includes comprehensive sales materials, demo scripts, competitive comparison guides, objection-handling frameworks, and extensive training programs that help sales representatives engage prospects successfully.
The objective with sales enablement is ensuring salespeople understand the product’s value proposition thoroughly and can navigate customer conversations effectively throughout the entire buyer’s journey.
Sales managers benefit from this strategy as it creates consistency and improves team performance across all customer interactions.

Channel Partner Strategy
This strategy enables distributors, resellers, or agencies to sell your products successfully through established distribution networks.
Companies focus on partner recruitment, comprehensive onboarding processes, ongoing training programs, co-marketing campaigns, and attractive incentive programs that expand their market reach.
The goal is making it easy and profitable for partners to represent and sell your products to their existing customer base while maintaining brand consistency and quality standards.
This distribution model works particularly well for companies looking to scale rapidly without building internal sales capabilities.
Product-Led Growth Strategy
This approach lets the product demonstrate its own value through direct customer experience, often reducing the need for extensive sales efforts and traditional marketing campaigns.
This product-led growth strategy includes free trials, freemium models (basic version free, premium features paid), seamless onboarding processes, and data-driven product improvements based on user behavior.
Companies using this method believe that exceptional product experience drives higher conversion rates than traditional sales methods while building stronger customer retention and advocacy.
The product-led GTM strategy has become increasingly popular among software companies seeking to minimize customer acquisition costs.
5 Go-to-Market Strategy Examples to Inspire You
Learning from successful companies provides valuable insights for crafting your own market strategy.
These market strategy examples demonstrate how different approaches can achieve remarkable results when properly executed, each addressing unique challenges and market conditions.
Every company faced specific obstacles and developed creative solutions that resonated with their target audience while achieving their business objectives and establishing strong market positions.
Example #1: Visme’s Desktop Launch
Visme, a graphic design platform, launched their desktop application in early 2021 with a focused approach.
The company needed to raise brand awareness for their new design platform compatible with both Mac and Windows, targeting design professionals and businesses seeking comprehensive design solutions.

Their go-to-market strategy centered on Product Hunt, a platform where tech enthusiasts discover and share new products.
Visme strategically timed their launch to generate buzz and attract their ideal customers through this specialized channel.
The timing and execution proved crucial for maximum impact and demonstrated how a well-planned go-to-market process can amplify results.
Visme’s founder, Payman Taei, amplified the launch through his personal LinkedIn network, showing how founder-led marketing can enhance traditional campaigns.
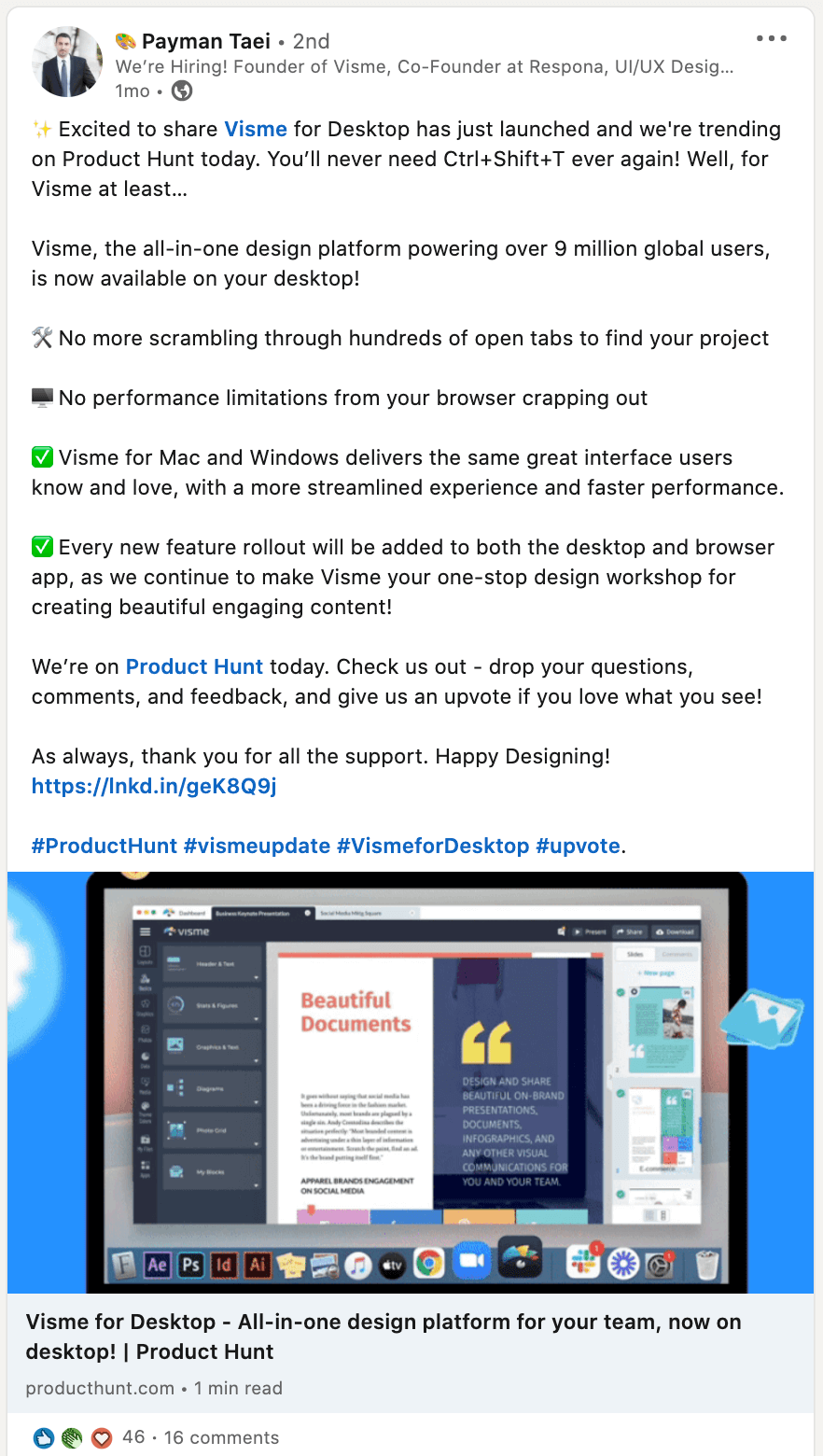
His posts included specific information about the product’s use cases and problems it solved for potential customers.
This personal touch added authenticity and credibility while building stronger customer connections and supporting their overall marketing strategy.
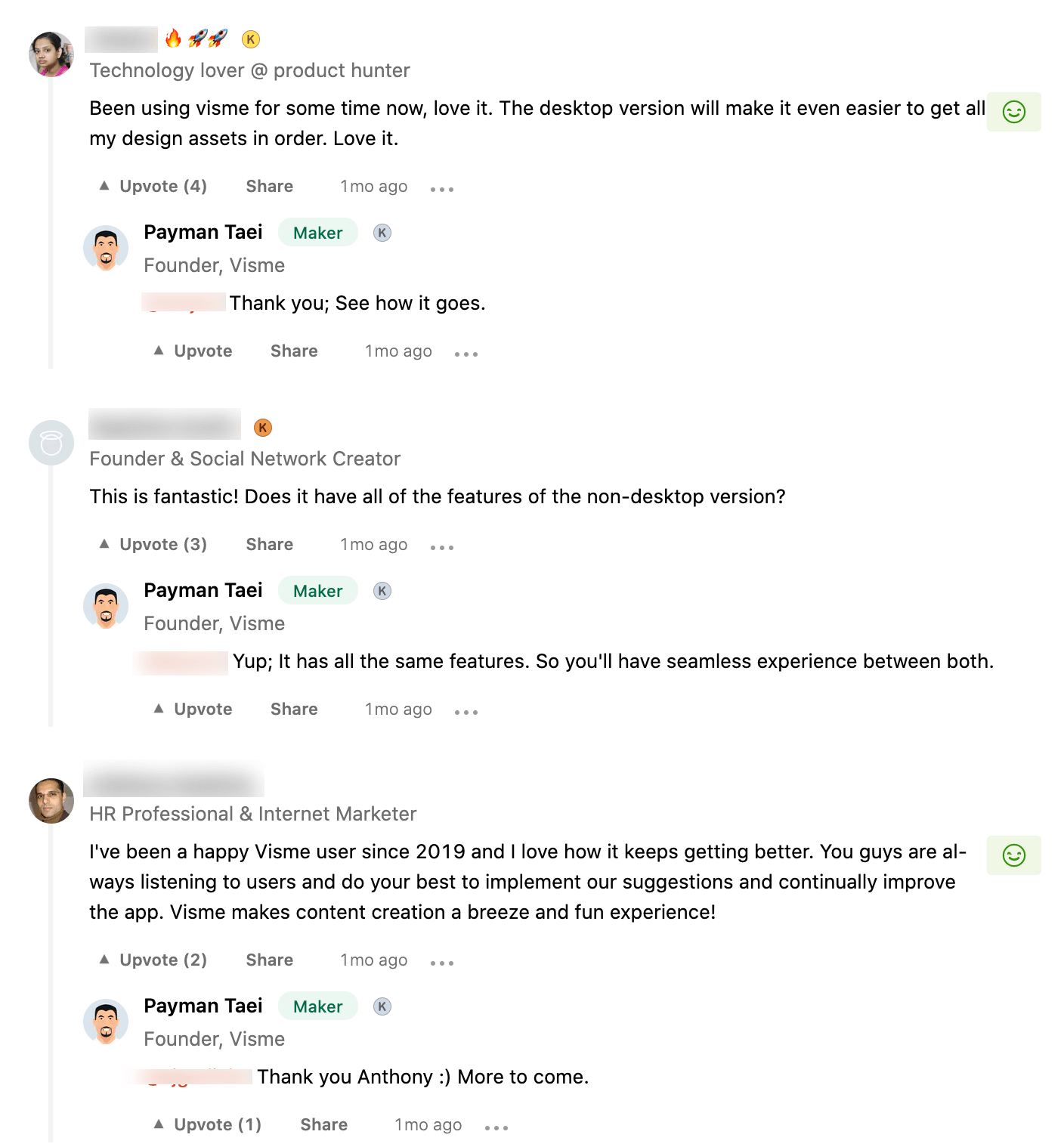
The Product Hunt presentation showcased detailed images of the desktop application’s interface, addressing common customer pain points through visual demonstration.
This approach helped future customers understand the product’s capabilities before making decisions, reducing barriers to adoption and supporting their sales strategy.
The strategy succeeded remarkably well—Visme’s desktop app was voted Product of the Day on April 13, 2021.
Enthusiastic user comments validated the product’s unique value proposition and market fit, proving that well-executed positioning can drive successful outcomes even in competitive markets.
Example #2: Challenger Bank Monzo’s Launch
Monzo, an app-based challenger bank established in the UK in 2015, faced the challenge of entering a banking market dominated by traditional institutions.
Established banks had significant advantages through brand recognition and existing customers, making customer acquisition extremely challenging for newcomers attempting to build their customer base.
Their groundbreaking GTM strategy revolved around creating exclusivity through a strategic waitlist system that turned customer acquisition into a game.
New users joined a queue with over 15,000 people registered before them, creating anticipation and making the product seem highly desirable.
This transformed the typical buying process into an engaging experience that built community before launch.
The genius lay in their referral mechanism that encouraged viral growth and reduced customer acquisition costs significantly.
Users could move up the queue by sharing their unique referral code with others, and every successful referral moved the sharer up several thousand places in line.
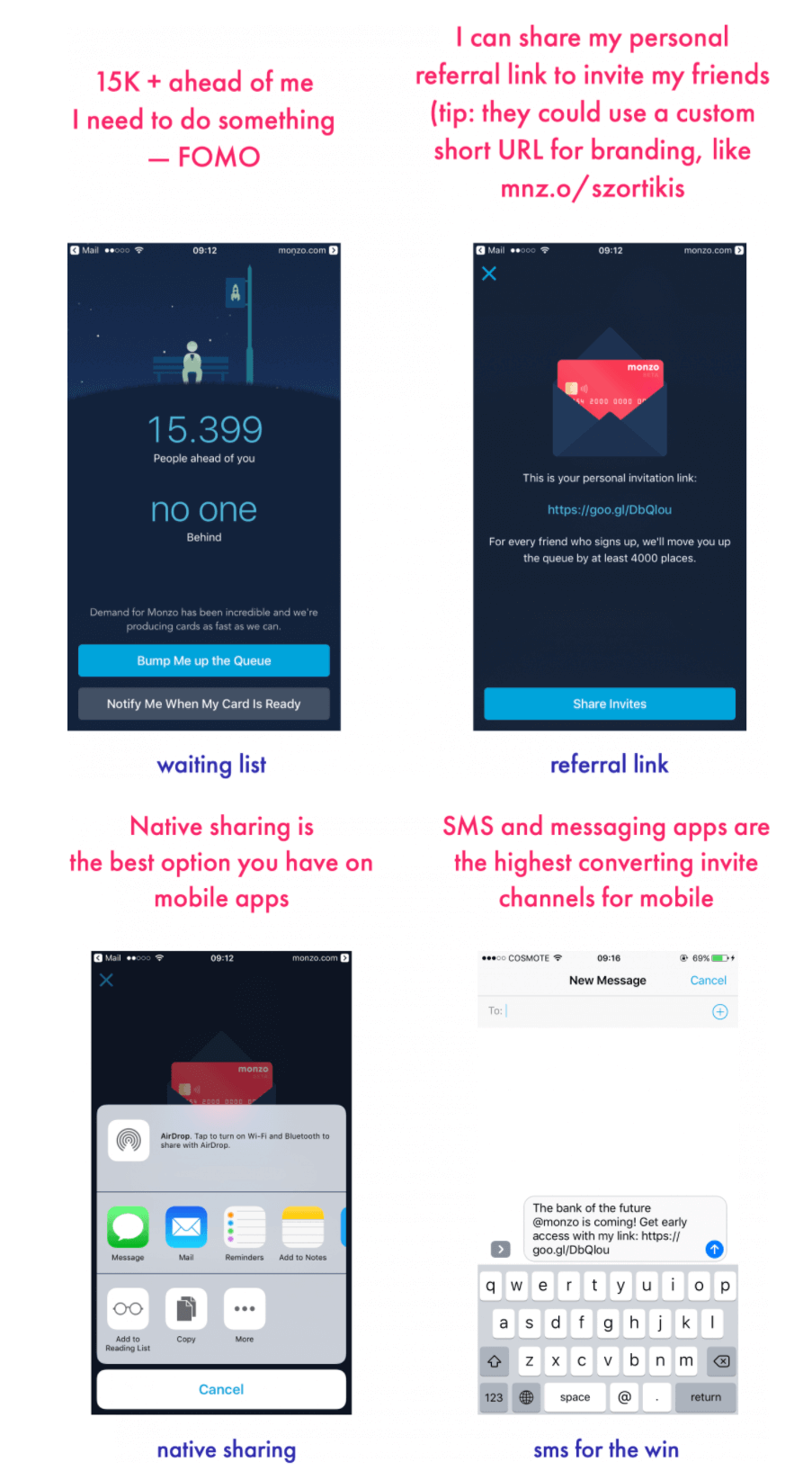
This gamification encouraged viral sharing and organic growth while significantly reducing customer acquisition costs.
Modern referral marketing platforms like Viral Loops make it easier for companies to implement similar gamified referral systems.
The strategy incorporated community marketing and pre-launch buzz that made users feel invested before even using the product.
The waiting list created exclusivity and insider access that traditional marketing couldn’t achieve, building strong customer relationships even before launch and establishing a foundation for future customer retention.
Initial launches targeted London residents specifically, making the experience focused and tailored to local conditions.
This geographic limitation helped create manageable growth while building strong local communities that provided valuable market feedback.
Since their Alpha launch in 2015, Monzo achieved revenues of £67million in 2019, proving that creative GTM strategies can overcome significant competitive disadvantages.
Example #3: Robinhood’s Pre-launch Strategy
Robinhood entered the stock market access space in 2014 with a mission to democratize finance for underserved customers.
The small startup faced established competitors with significant resources and brand recognition.
Their target audience was millennials who lacked access to affordable investing platforms, representing an underserved market opportunity with substantial growth potential.
Their innovative go-to-market strategy emphasized creating a VIP experience that built anticipation and fear of missing out (FOMO) among potential customers.
The company turned access into a game, making it feel exclusive and valuable while encouraging word-of-mouth marketing.
Early adopters became advocates before even using the platform, demonstrating how effective positioning can turn prospects into promoters.
A signup waiting list with strong referral incentives drove early customer acquisition while building community engagement.
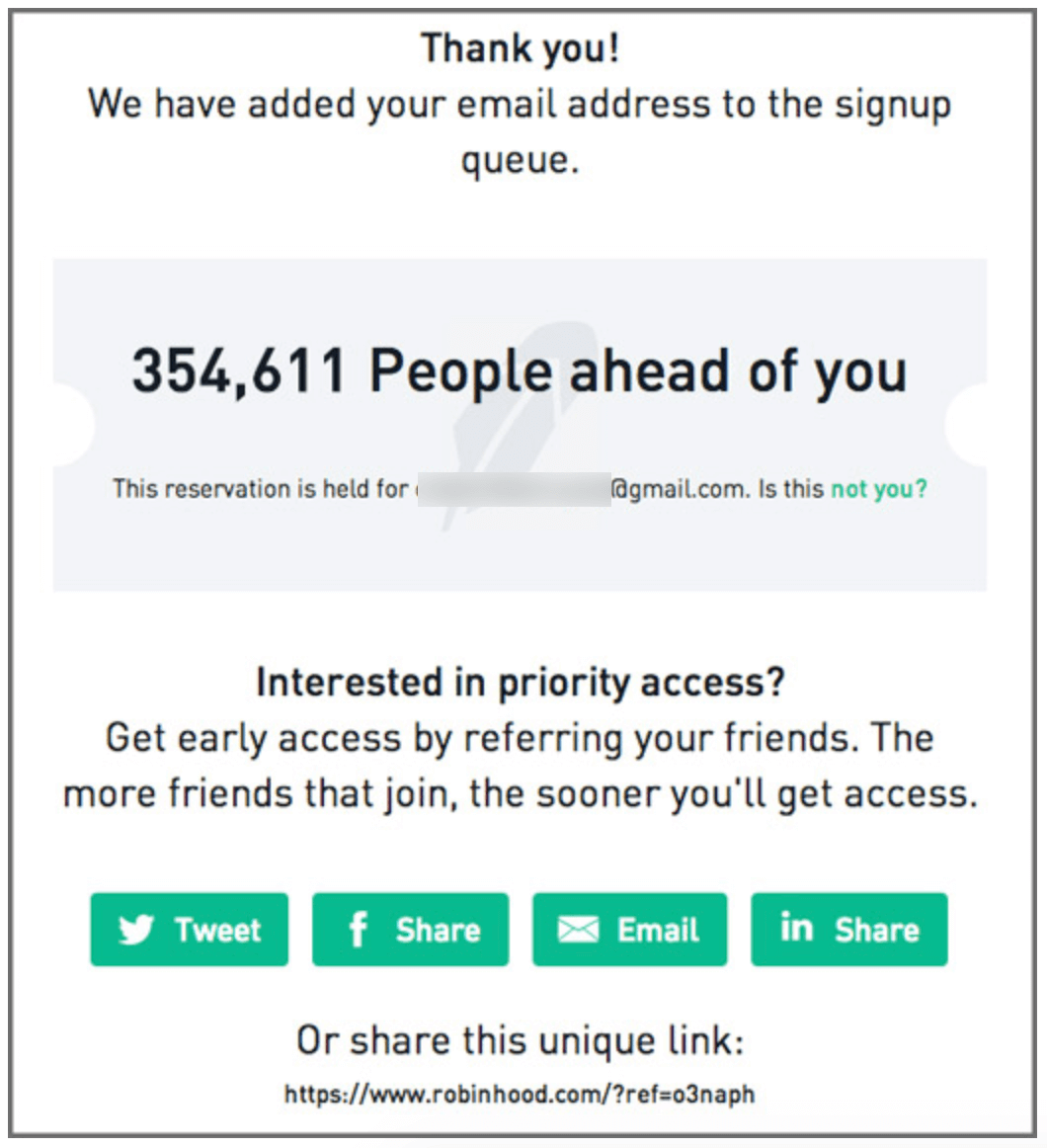
Users could gain priority access by inviting friends to join the queue—the more friends who joined, the sooner users would gain access.
Today’s referral marketing platforms like Viral Loops offer similar functionality for companies looking to replicate this viral growth model and implement effective go-to-market strategies.
This referral-driven approach made users feel the product was exclusive while encouraging them to spread awareness through their personal networks.
The combination of exclusivity and social sharing created powerful word-of-mouth marketing that traditional advertising couldn’t match.
Users became invested in the platform’s success because they helped build its community, leading to stronger customer retention and advocacy.
Give it a try for yourself. Sign up for a free trial.
Example #4: TaxJar’s Content-Focused Approach
TaxJar, launched in 2013, brought automation to sales tax reporting for e-commerce businesses operating in multiple markets.
The company identified a key competitive advantage early through comprehensive market research.
CEO Mark Faggiano recognized that existing sales tax content was either hard to find or difficult to understand, creating an opportunity to establish thought leadership.
Their content-focused marketing strategy centered on educating the market through accessible, high-quality content that addressed specific customer problems.
The company positioned itself as a technology company rather than a traditional tax service, differentiating from competitors who focused purely on compliance.
This positioning helped them attract tech-savvy businesses looking for modern solutions while building their reputation as industry experts.
TaxJar created comprehensive content addressing sales tax challenges across different industries.
They published articles like “Sales Tax for Telehealth Services” and “Online Pharmacy Tax Requirements” that targeted specific buyer types and customer segments.
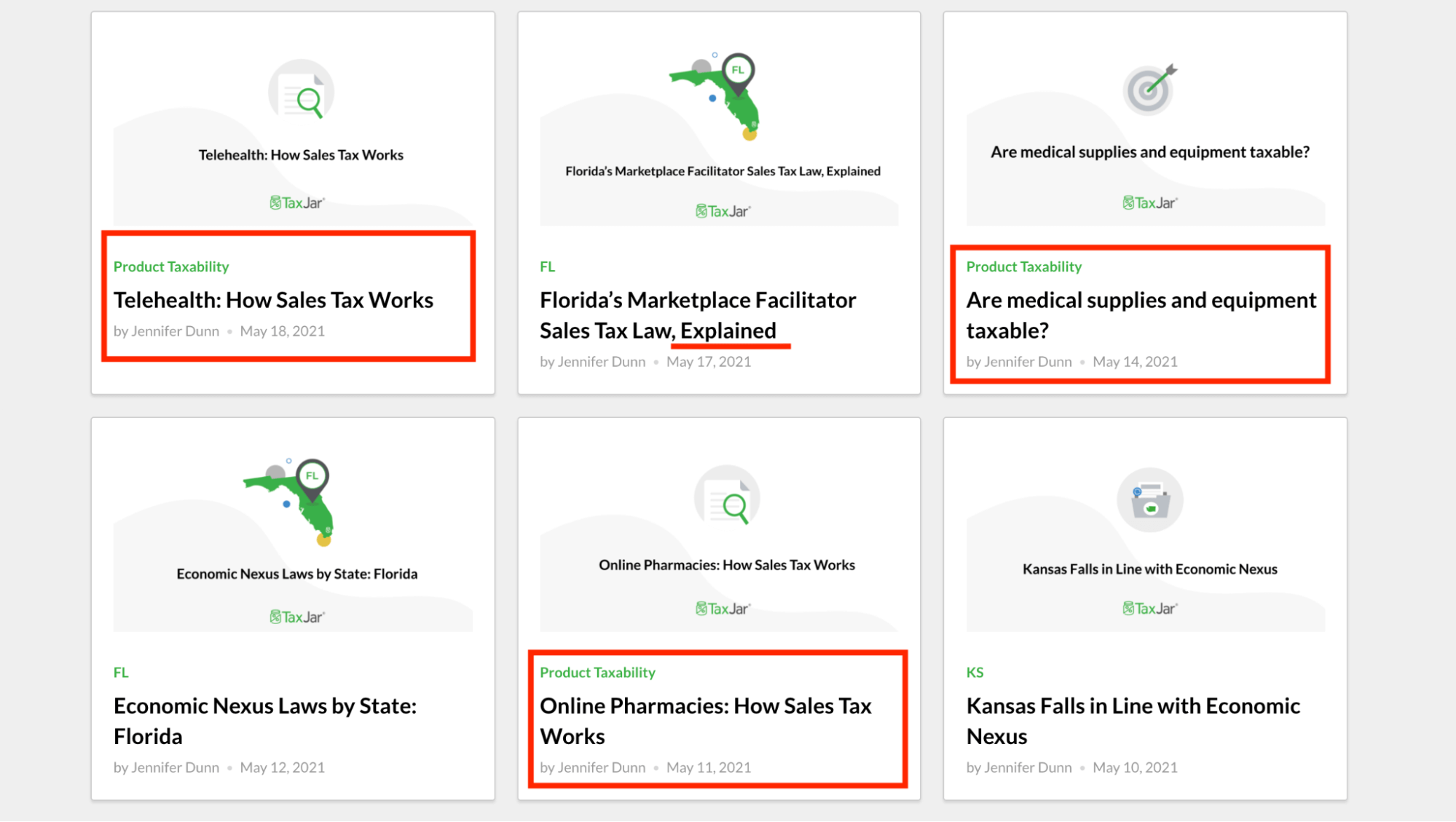
This industry-specific approach attracted businesses seeking relevant guidance while establishing TaxJar as the authority in their space.
The content marketing strategy built trust with potential customers before they needed the product, nurturing long-term customer relationships.
Users discovered TaxJar through educational searches and developed confidence in the company’s expertise before entering the buying process.
This approach generated word-of-mouth referrals and organic growth while reducing customer acquisition costs and supporting their overall sales strategy.
As Mark Faggiano explained, “We decided to build the best content we could to help people wrap their heads around sales tax, which feels like an insane problem that’s changing constantly.”
The strategy helped establish TaxJar as the go-to resource for sales tax education, proving that educational content marketing can be a powerful competitive advantage when executed consistently.
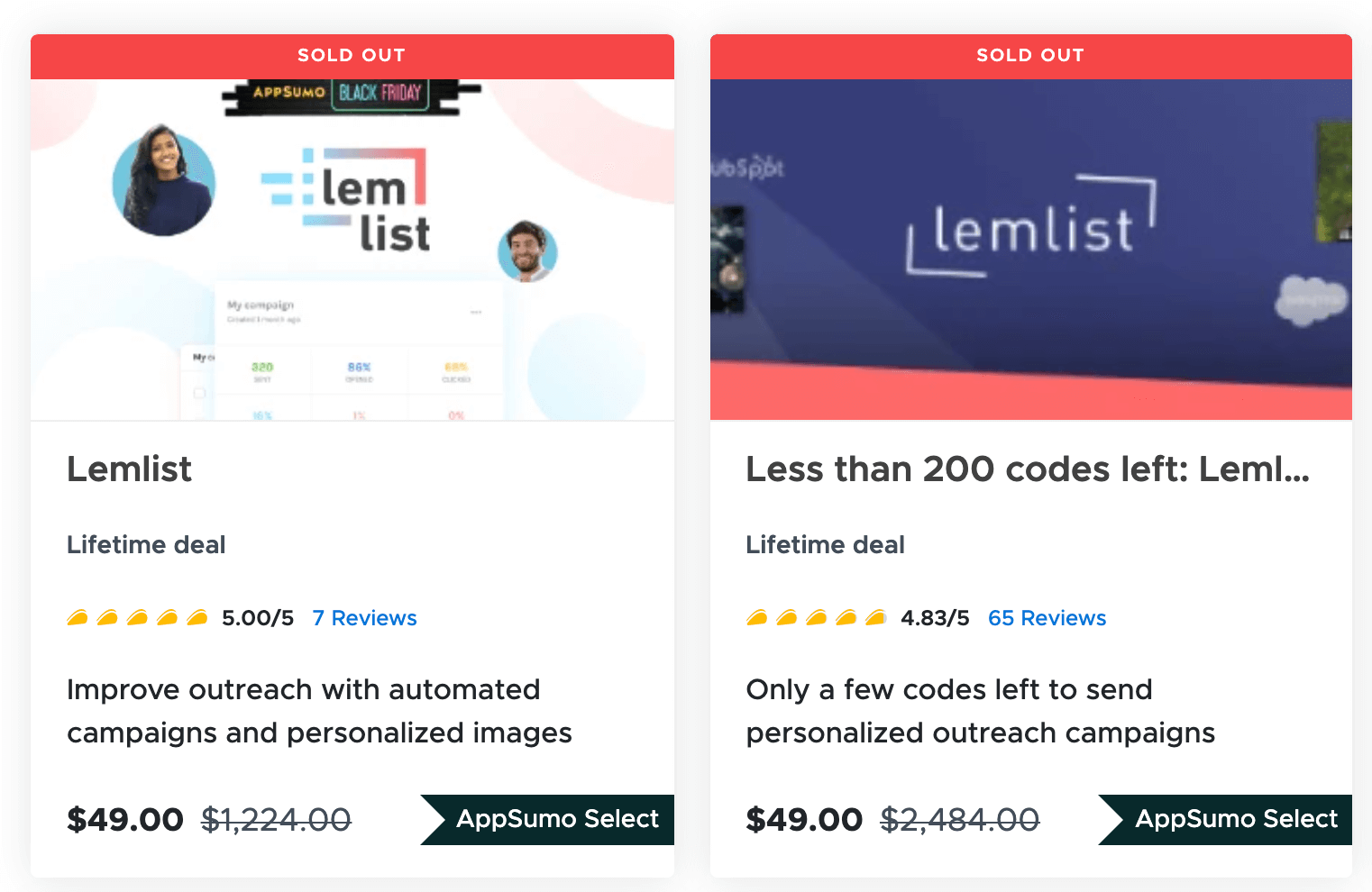
Example #5: Lemlist’s Marketplace Launch
Lemlist, an email outreach platform for personalized campaigns, launched on Appsumo in early 2018 with a marketplace-focused approach.
The company needed rapid customer acquisition and revenue generation while competing in a crowded market to fuel product development.
Appsumo, a marketplace for early-stage startups, offered the perfect distribution model for reaching their target customers.
The main element of Lemlist’s go-to-market strategy involved offering special deals through Appsumo’s marketplace to reach new customer segments quickly.
Startups can offer lifetime access deals at significantly reduced prices to generate quick revenue while building their customer base.
This approach allows new companies to acquire customers while funding continued development, addressing both immediate and long-term business objectives.
Lemlist went on Appsumo twice in their first year, including a Black Friday deal that expanded their reach to bargain-seeking customers.
The marketplace strategy provided immediate capital that could be reinvested into product development and business growth—especially valuable for resource-constrained startups looking to optimize their customer acquisition costs and establish market presence.
The company also leveraged Product Hunt to generate additional buzz from the tech community, demonstrating how multiple marketing channels can amplify results.
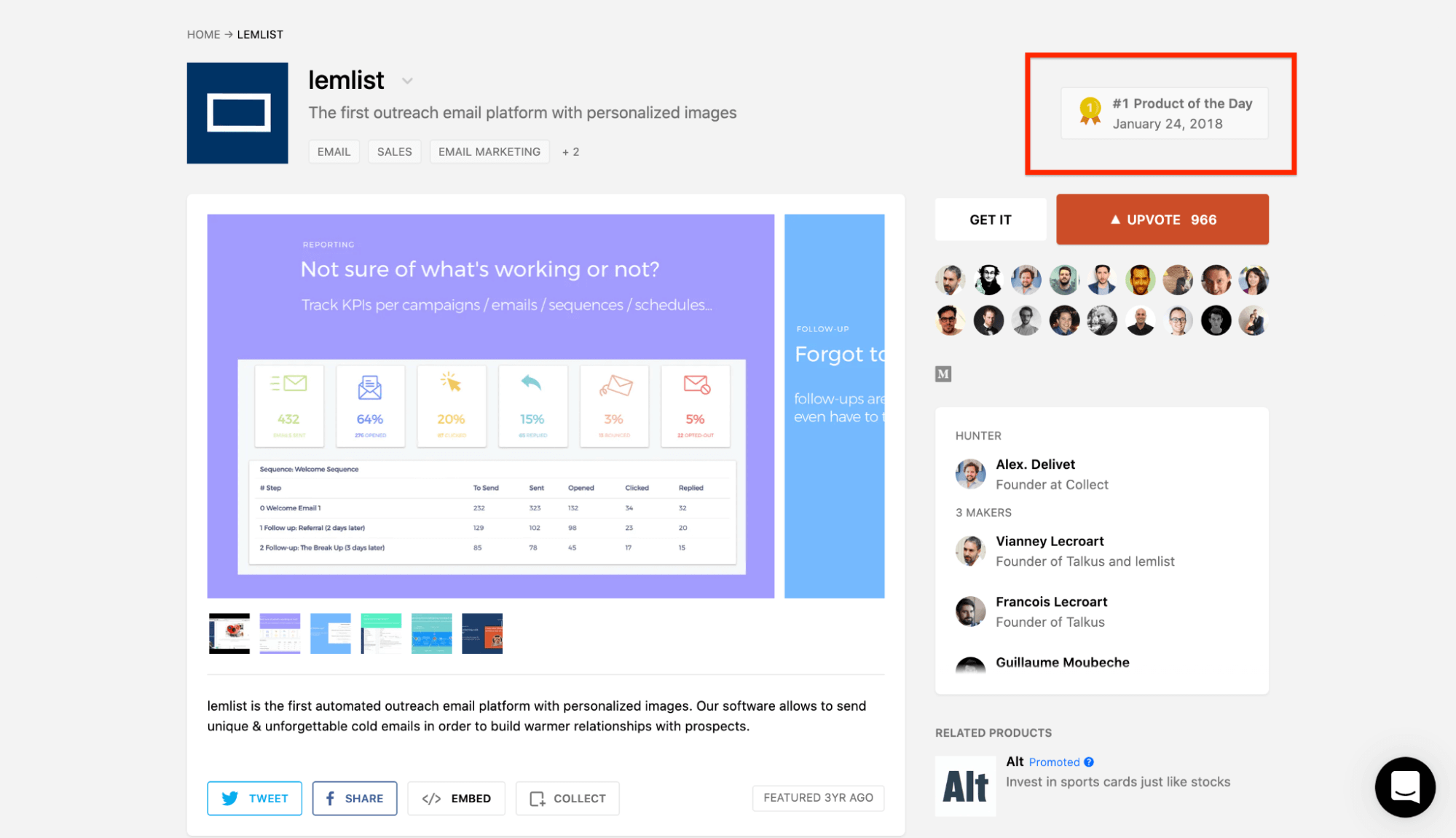
Their product was voted Product of the Day on January 24, 2018, providing social proof and validation that helped attract users beyond the Appsumo customer base.
The combined approach of marketplace deals and community recognition created multiple touchpoints for customer acquisition across different distribution channels.
Lemlist achieved $250K annual recurring revenue in 2018, growing to over $4 million by early 2021 with plans to reach $10 million.
This growth trajectory demonstrates how strategic channel selection can accelerate business growth when aligned with target market preferences.
How to Build a Go-to-Market Strategy for Your Startup
Creating an effective go-to-market strategy requires systematic planning and careful execution across multiple business functions.
Startups especially need well-organized approaches since resources are limited and mistakes can be costly.
The following step-by-step go-to-market process provides a framework for building successful strategies that align your marketing and sales teams around common business objectives.
Step #1: Understand Your Target Market
The first step involves comprehensive conducting market research to understand your competitive landscape and identify opportunities for gaining competitive advantage in your chosen market.

Your target market represents the segment of potential customers your product will target most effectively based on demographics, behaviors, and needs.
Understanding this group’s characteristics, preferences, and pain points allows you to craft common sales strategies, pricing approaches, and customer experiences that resonate with their specific needs and problems while differentiating from competitors.
Market research requires multiple analytical approaches to examine competitors, identify potential partnerships, assess market size and growth potential, and thoroughly evaluate current market conditions.
This foundational work prevents costly mistakes and identifies opportunities for differentiation that can become your unique value proposition.
Effective market research also helps you understand your target customers’ buying process, decision-making criteria, and how to optimize your sales funnel accordingly for maximum conversion.
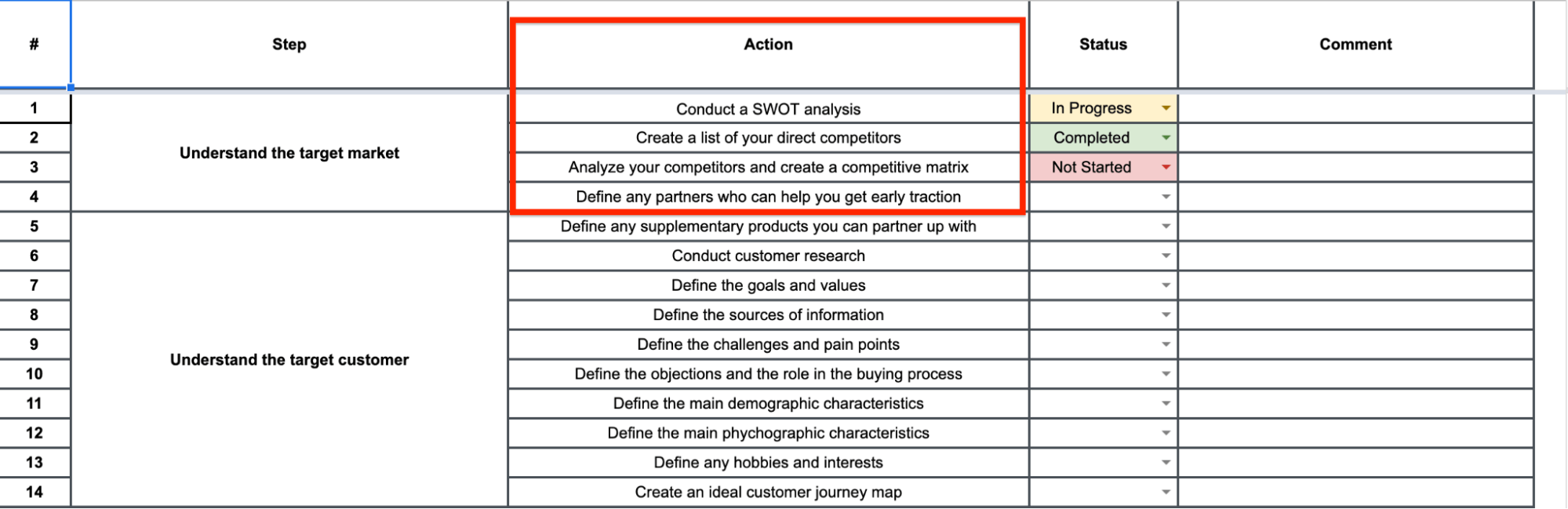
Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Evaluate your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats objectively in relation to your target market.
This analysis helps identify competitive advantages and potential challenges before launch while informing your overall marketing strategy.
Understanding your position relative to market conditions guides strategic decision-making and helps you allocate resources effectively across your marketing team.
Create a List of Your Direct Competitors
Research companies operating in your target space to understand the competitive landscape thoroughly.
Examine their offerings, pricing strategy, positioning, and customer feedback to identify gaps in the market.
This information helps craft compelling value propositions and reveals potential partnership opportunities that could enhance your distribution model.
Develop a Competitive Analysis Matrix
Create systematic comparisons of features, pricing strategy, and positioning across your target market.
Understanding competitor strengths and weaknesses helps develop messaging that highlights your competitive advantage effectively.
This analysis also reveals market gaps where you can position your product or service uniquely.
Identify Potential Partners and Collaborators
Expand your reach and credibility through strategic partnerships.
These collaborations can provide access to existing customers, established distribution channels, or complementary capabilities that reduce customer acquisition costs.
Early-stage companies especially benefit from partnership-driven growth strategies that leverage existing customer relationships.

Step #2: Understand Your Target Customer
Following comprehensive market research, focus on understanding your specific target customers in detail through buyer persona development.
This step involves creating detailed profiles of people most likely to become loyal customers and advocates for your product or service.
Deep customer understanding enables product development that meets real needs and marketing efforts that resonate authentically.
Customer research goes beyond basic demographics to include behavioral patterns and decision-making processes that influence purchasing.
The goal is understanding not just who your potential customers are, but why they make purchasing decisions and what problems drive them to seek solutions.
This understanding becomes crucial for developing effective sales strategies and optimizing the customer experience.
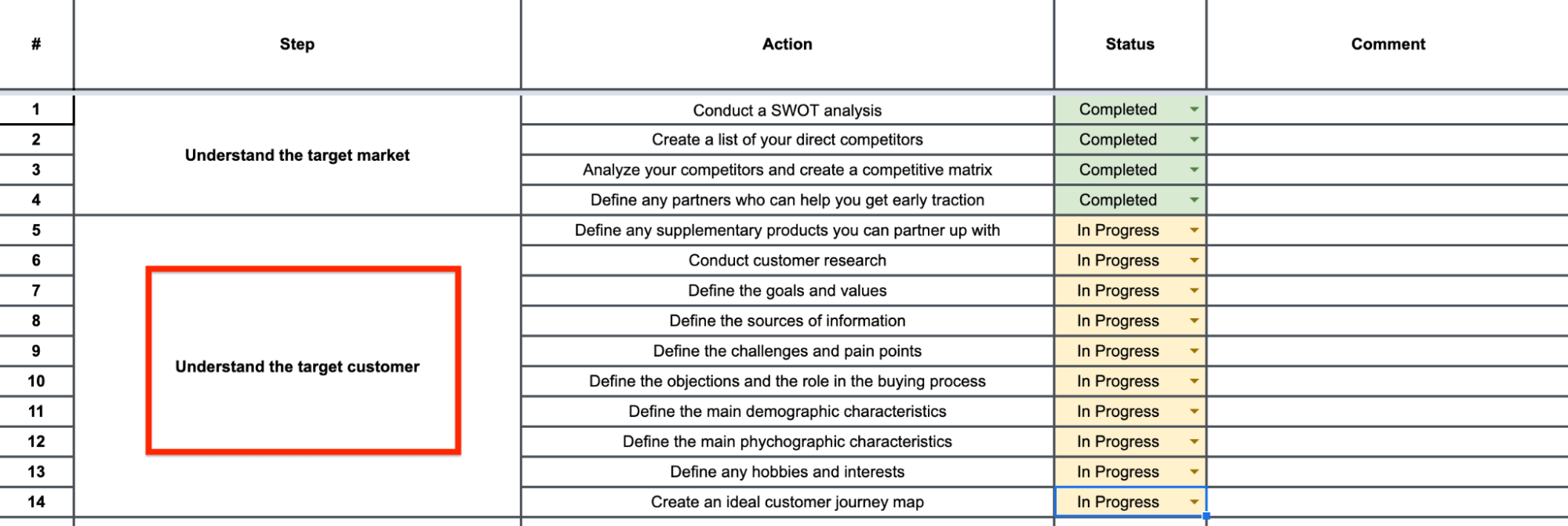
Conduct Detailed Research into Your Ideal Customer Profile
Use surveys, interviews, and behavioral analysis to reveal true customer motivations.
Primary research provides insights that secondary data cannot capture about your target customers’ real needs and preferences.
Understanding customer motivations, frustrations, and aspirations guides both product development and marketing strategy decisions while helping your sales team connect more effectively with prospective customers.
Define Your Goals and Value Matrix
Map customer problems to your product’s capabilities and unique value proposition.
This exercise clarifies how your solution creates value for specific customer segments while differentiating from competitors.
Clear value articulation becomes the foundation for sales and marketing messaging that resonates with prospective customers and supports effective sales strategies.
Conduct Demographic and Psychographic Analysis
Understand customer characteristics, preferences, and behaviors that influence their purchasing decisions.
Demographics provide basic segmentation while psychographics reveal deeper motivations and values that drive customer relationships.
Both perspectives are necessary for comprehensive customer understanding and developing targeted marketing campaigns.
Define Potential Pain Points and Challenges
Complete honest assessment of potential objections or concerns allows proactive addressing in marketing materials and sales conversations.
Understanding these pain points improves sales team effectiveness and conversion rates while reducing customer acquisition costs through better qualification and more focused sales efforts.
Create an Ideal Customer Journey Map
Trace the path from problem recognition to purchase decision across all touchpoints.
Journey mapping reveals critical moments where marketing can influence decisions and optimize the customer experience.
Understanding the customer’s journey helps optimize each interaction for maximum impact and supports better alignment between marketing and sales teams.
Step #3: Define Your Positioning
Positioning determines how your product fits into the market landscape and customer minds relative to competitors.
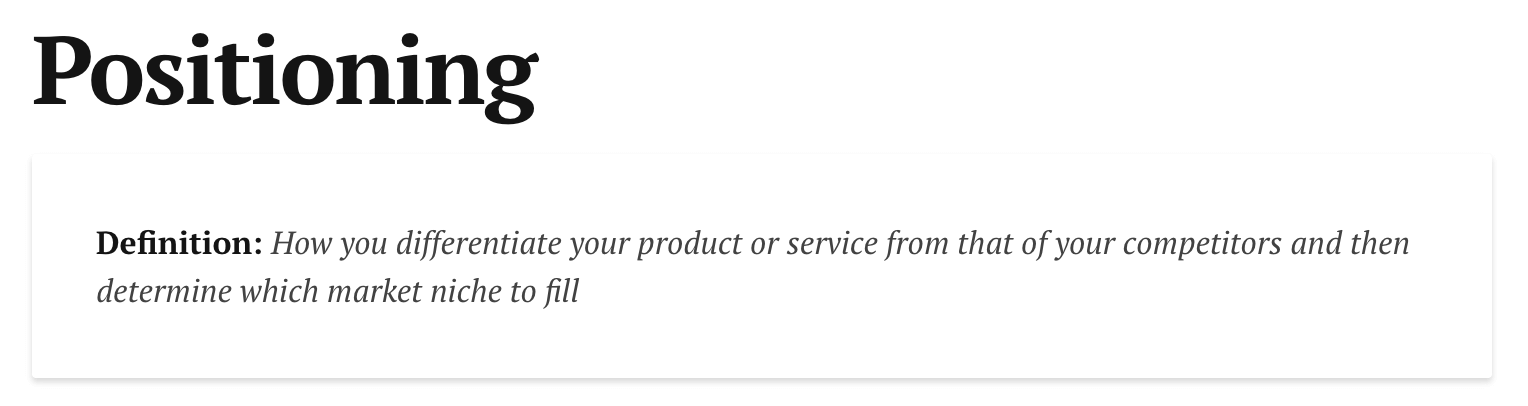
Effective positioning differentiates your offering from alternatives while resonating with target customers and supporting your unique value proposition.
This step requires balancing market realities with customer perceptions and competitive dynamics.
Positioning influences product development, pricing strategy, distribution channel selection, and customer experience decisions across your organization.
Consistent positioning across all touchpoints builds brand recognition and customer trust while making marketing efforts more effective and supporting your overall go-to-market strategy.
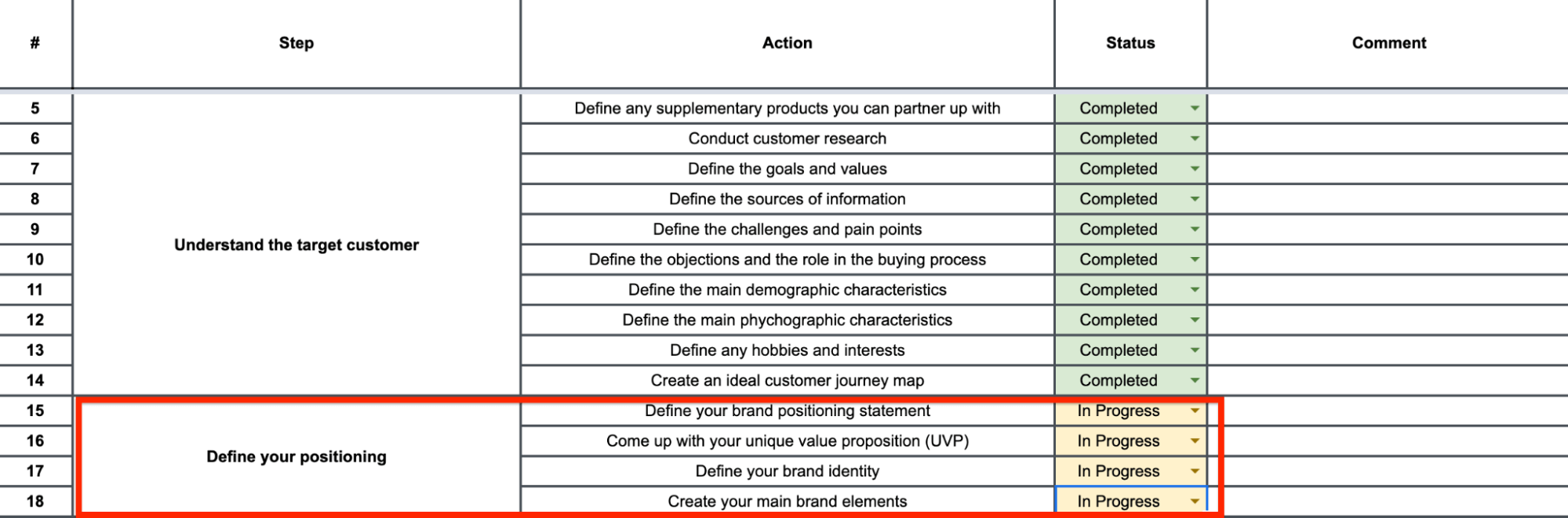
Define Your Brand Positioning Statement
Clearly articulate your unique value in the market that resonates with your target audience. This statement becomes the foundation for all marketing communications and strategic decisions.
A strong positioning statement differentiates while remaining authentic and achievable, supporting long-term customer relationships and effective marketing campaigns.
Develop Your Unique Value Proposition
Explain why customers should choose your solution over alternatives in the market.
Your value proposition should address specific customer pain points better than competitors while highlighting your competitive advantage.
Clear value propositions make sales conversations more focused and effective while supporting higher conversion rates and reducing the sales cycle length.
Define Your Unique Brand Odentity
Reflect your positioning and resonate with target customers across all marketing channels.
Brand identity encompasses visual elements, tone of voice, and personality traits that differentiate your company.
Consistent identity builds recognition and emotional connections with customers while supporting effective go-to-market strategies.
Create Your Main Branding Elements
Include logos, color schemes, typography, and messaging frameworks that support your positioning.
These elements should reinforce your unique value proposition while appealing to target customers’ preferences and expectations.
Professional branding increases credibility and supports effective marketing campaigns across all customer touchpoints.
Step #4: Define Your Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy translates positioning into actionable plans for reaching and converting potential customers across multiple touchpoints.
This step involves selecting appropriate marketing channels, developing content that resonates with buyer personas, setting pricing strategy, and creating measurement frameworks that track progress toward business objectives.
A comprehensive marketing plan ensures all marketing efforts work together cohesively.

Modern marketing strategies integrate multiple channels and touchpoints to create cohesive customer experiences that guide prospects through awareness, consideration, and decision stages efficiently.
The goal is nurturing customer relationships while driving conversions and supporting long-term customer retention.
Effective strategies also consider how to measure success through appropriate key performance indicators.
Define Your Pre-launch Campaign
Build anticipation among target customers before your product becomes available.
Pre-launch campaigns create awareness, generate early interest, and build communities around your upcoming offering.
This phase often includes content marketing, social media engagement, and email list building that primes your target market for launch while supporting your overall go-to-market strategy.
Define Your Launch Campaign
Drive initial adoption and market penetration during your official product launch.
Launch campaigns typically feature coordinated marketing efforts across multiple marketing channels, press releases, and promotional activities.
The goal is maximizing visibility and converting early adopters who can become advocates while establishing your presence in the existing market.
Define Your Post-Launch Campaign
Sustain momentum after launch while supporting customer retention and advocacy.
Post-launch campaigns focus on customer success, referral programs, and continuous engagement that builds long-term customer relationships.
Referral marketing tools like Viral Loops can help automate and scale these word-of-mouth campaigns effectively while reducing ongoing customer acquisition costs.
Define Your Complete Marketing Funnel
Create systematic approaches for converting prospective customers into loyal advocates through optimized customer experiences.
Effective sales funnels address customer needs at each stage while moving them toward purchase decisions and long-term relationships.
Well-designed funnels improve conversion rates while reducing customer acquisition costs and supporting scalable growth across your customer base.
Our Proven Go-to-Market Strategy Template
Creating a comprehensive go-to-market strategy from scratch can feel overwhelming, especially for first-time entrepreneurs managing limited resources.
That’s why we’ve developed a comprehensive template that streamlines the planning process while ensuring you address all critical elements of a successful GTM strategy.
Our template systematically guides you through each critical step, from market research to execution planning and success measurement.
It includes sections for competitive analysis, customer research, positioning development, and tactical planning that support effective go-to-market execution.
The structured approach ensures you don’t miss important considerations while focusing on actionable steps that drive results and help establish a solid GTM strategy.
The template features dropdown menus for tracking progress through different phases of your go-to-market process.
Status options include Completed, In Progress, and Not Started for easy project management and team coordination.
This functionality helps marketing and sales teams stay organized and accountable throughout the planning process while ensuring everyone understands their role in the successful GTM strategy implementation.
Comments sections allow additional notes and insights to be captured alongside each element, supporting knowledge sharing among team members.
This feature enables teams to document decisions, rationale, and lessons learned for future reference while building organizational knowledge.
Teams can track assumptions, test results, and optimization opportunities that inform ongoing strategy refinement and help measure success effectively.
The template serves as both planning tool and reference document throughout your go-to-market execution and optimization phases.
Regular updates keep the strategy current and actionable while supporting continuous improvement based on market feedback.
Download the template today to accelerate your go-to-market planning and increase your chances of achieving a successful product launch.
Time to Get Started!
Building a successful go-to-market strategy requires systematic planning, deep customer understanding, and tactical execution that aligns your marketing and sales teams around common business objectives.
Whether you’re launching a new product in an existing market or entering a new market entirely, these principles provide a solid foundation for success.
Remember that effective go-to-market strategies are living documents that should evolve based on market feedback and performance data from your marketing campaigns.
Start with solid research and planning, but remain flexible enough to adapt as you learn more about your target customers and market conditions.
The most successful companies iterate their strategies based on real-world results while staying focused on their core business objectives and maintaining strong customer relationships.
The template and market strategy examples provided here give you practical tools for implementing your own go-to-market strategy while avoiding common pitfalls that increase customer acquisition costs.
Don’t let analysis paralysis prevent you from taking action—start with what you know and refine as you go.
Success comes from consistent execution and continuous improvement, not perfect initial planning that delays market entry and product launch timing.
Ready to build your winning go-to-market strategy and achieve a successful product launch? Download our proven template and start planning your path to market success today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a GTM strategy?
A go-to-market strategy is a tactical plan that outlines how a company will reach target customers and achieve competitive advantage when launching a new product or entering a new market.
It includes customer identification, positioning, messaging, pricing strategy, distribution channels, and key performance indicators to measure success across all marketing efforts.
What are the 7 GTM motions?
The seven go-to-market motions are product-led growth, sales-led growth, marketing-led growth, partner-led growth, community-led growth, brand-led growth, and founder-led growth.
Each motion represents a different approach to customer acquisition and retention based on your business model, resources, and target market characteristics.
Understanding these different approaches helps companies choose the most effective go-to-market model for their specific situation.
What are the four P’s of GTM?
The four P’s of go-to-market strategy are Product (what you’re selling), Price (your pricing strategy), Place (distribution channels and target market), and Promotion (marketing efforts and campaigns).
These elements work together to create a comprehensive approach to market entry and customer acquisition that supports business objectives and helps establish competitive advantage.
What is a go-to-market strategy model?
A go-to-market model is a framework that guides how companies bring products to market systematically while optimizing customer acquisition costs.
It typically includes customer segmentation, value proposition development, channel selection, pricing strategy, and performance measurement to ensure successful market entry and sustainable growth across the customer base.

1 comment
Great checklist to ensure you are not blindfolded in your GTM strategy.